Computer parts encompass both hardware and software components, each playing vital roles in the functionality and operation of a computer system.
Hardware Components:
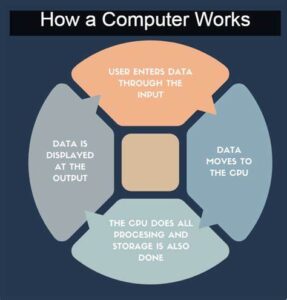
Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the brain of the computer, the CPU executes instructions, performs calculations, and manages data. It consists of an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit.
Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board of the computer, providing the platform for other hardware components to connect and communicate with each other. It houses the CPU, memory, and other essential components.
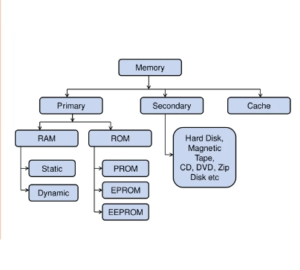
Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM temporarily stores data that the CPU needs to access quickly. It is volatile memory, meaning it loses its contents when the power is turned off. More RAM allows for smoother multitasking and faster performance.
Storage Devices: These devices store data permanently or temporarily. Common types include:
Hard Disk Drive (HDD): Uses spinning disks to store data magnetically.
Solid State Drive (SSD): Utilizes flash memory for faster data access compared to HDDs.
External Drives: USB drives, external HDDs, and SSDs for additional storage and portability.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Responsible for rendering images and videos, GPUs are crucial for gaming, graphic design, and video editing. They accelerate image processing and relieve the CPU of graphics-related tasks.
Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts electricity from the outlet into usable power for the computer components. It supplies the necessary voltages and currents to ensure smooth operation.
Input/Output (I/O) Devices: These devices facilitate communication between the user and the computer:
Keyboard and Mouse: Input devices for typing and pointing, respectively.
Monitor: Displays visual output from the computer.
Printer and Scanner: Devices for printing documents and scanning images, respectively.
Speakers and Microphone: For audio input and output.
Cooling System: Prevents overheating of computer components by dissipating heat generated during operation. Common cooling systems include fans, heat sinks, and liquid cooling solutions.
Software Components:
Operating System (OS): The OS manages computer hardware and provides a user interface for interacting with the system. Popular OS options include Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Device Drivers: These software programs allow the OS to communicate with and control hardware devices. They facilitate proper functioning and compatibility between hardware components and the OS.
Applications: Software applications perform specific tasks based on user inputs. They include productivity tools (e.g., word processors, spreadsheets), multimedia software (e.g., video players, photo editors), and utilities (e.g., antivirus programs, file management tools).
Firmware: Firmware resides on hardware components and provides low-level control and functionality. Examples include BIOS/UEFI firmware on the motherboard and firmware on peripherals like printers and routers.
Utilities: These software programs perform system maintenance tasks, optimize performance, and troubleshoot issues. Examples include disk cleanup tools, antivirus software, and backup utilities.
Understanding the roles and interactions of hardware and software components is essential for effectively using and maintaining computer systems. Together, they form the foundation of modern computing technology, enabling a wide range of applications and functionalities.

This blog provides a clear and informative breakdown of computer hardware and software components. The detailed explanation of each part, from the CPU to storage devices and software applications, makes it easy to understand their roles in a computer system. A great read for anyone looking to learn more about how computers function!
Thank you INP Technologoies for your time.